|

"Yoga Breathing Techniques," known in Sanskrit as "Pranayama," consists of two parts: "Prana," which means life force or life energy, and "Ayama," which means expansion or extension. As the name suggests, breathing is fundamental to yoga, and practicing yoga breathing techniques is essential for entering a yogic state. Through breathing exercises, life energy flows and expands throughout the body. In yoga practice, conscious and controlled breathing guides the body through smooth, flowing movements, bringing vitality to both body and mind. Steady breath control also helps calm the mind, release tension, and deeply relax.
In Sanskrit, "Pranayama" refers to the act of breathing (breath control), and it is the fourth limb of the Eight Limbs of Yoga outlined in the ancient Yoga Sutras of Patanjali. By consciously applying different techniques, one can influence the flow, frequency, and volume of air in the respiratory system, allowing a connection between the mind, body, and subconscious.
The deeper you breathe, the deeper you move into the posture, and the more oxygen penetrates the muscles. For beginners, learning to coordinate breath with movement is the first crucial step in yoga practice. Without synchronizing breath with postures, it's difficult to fully immerse oneself in the practice. However, this takes time and gradual practice. So, before touching your toes, beginners must first learn the breathing techniques. By combining Pranayama (breath control) with Asana (postures), flexibility and physical strength will naturally increase.
During yoga practice, breath must be coordinated with movement: inhale to expand, exhale to relax. Prana (life force energy) and Apana (downward energy) are clearly evident here. Prana represents inhaling air into the body to nourish and heal, while Apana is the exhalation that expels waste from the body, symbolizing a downward or outward force of elimination. Focusing on breath is also used in relaxation exercises to calm a busy mind.
Benefits of Yoga Breathing Techniques:
1. Stabilizes emotions and relieves stress.
2. Revitalizes the body and boosts energy.
3. Clarifies the mind and enhances mental agility.
4. Calms the mind and improves focus.
5. Enhances empathy and self-awareness, fostering better interactions with others.
Types of Pranayama:
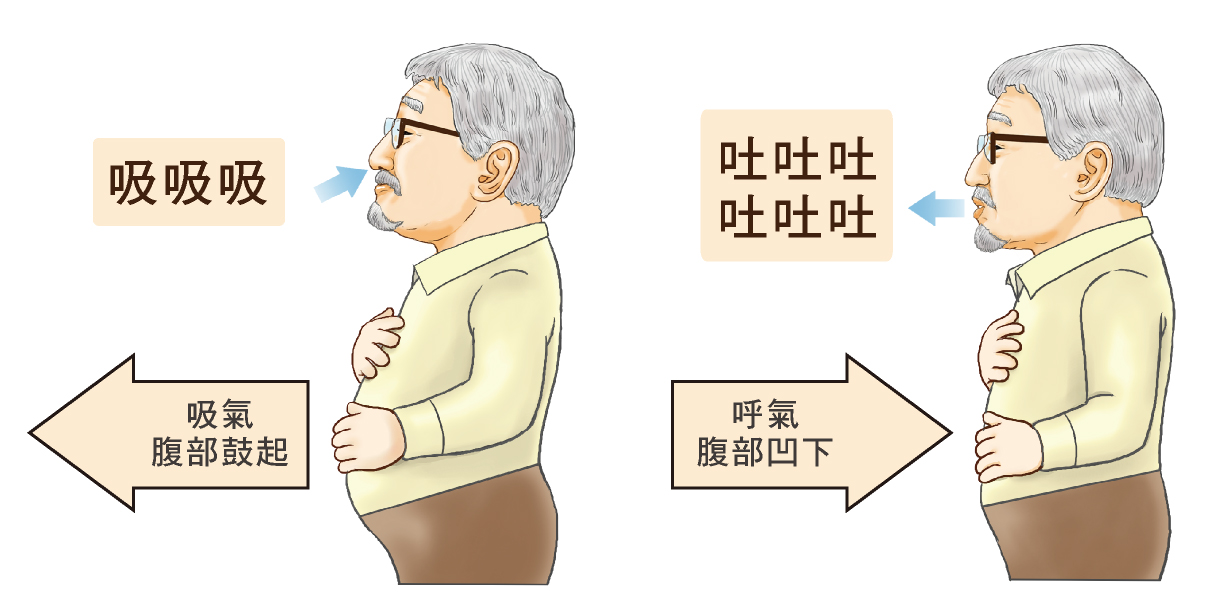 |
Abdominal Breathing (Diaphragmatic Breathing)
When you inhale, the abdomen expands, and when you exhale, it contracts naturally. This breathing technique focuses on the movement of the diaphragm. As you inhale, the diaphragm presses downward, expanding the chest cavity and allowing air to reach deeper into the lungs, providing them with sufficient oxygen.
Benefits of Abdominal Breathing
1. Stress Relief and Improved Sleep: By breathing slowly, you relax your muscles and alleviate fatigue, similar to the principle of deep breathing for emotional relief. Since stress can cause tension and insomnia, practicing abdominal breathing for a few minutes before bed can improve sleep quality.
2. Enhances Body Functions**: Abdominal breathing promotes effective gas exchange, increasing the body’s oxygen levels, improving blood circulation, and boosting metabolism. It also helps digestive functions and can prevent constipation.
3. Increases Lung Capacity: This type of breathing increases the amount of air your body can take in, which enhances lung capacity and endurance during exercise.
4. *Shifts Attention: Focusing on deep inhalation and exhalation can divert attention away from stress or tension, reducing anxiety.
5. Complete Gas Exchange: This technique allows for deeper inhalation of fresh air and full exhalation of stale air, aiding complete gas exchange in the body.
Practice Method:
1. Full Exhalation: Start with 1-2 full exhalations to empty your lungs, creating a vacuum for a deeper next breath.
2. Inhale Through the Nose, Exhale Through the Mouth: Begin by exhaling through the mouth, then slowly inhale through the nose. Once comfortable, switch to both inhaling and exhaling through the nose.
3. Visualize the Abdomen as a Balloon: Place your hands on your abdomen to feel it rise and fall with your breath.
4. Use Gentle Pressure on the Abdomen: If it’s hard to inhale deeply, use your hands to gently press your abdomen as you exhale, and then feel your abdomen push back up as you inhale.
|
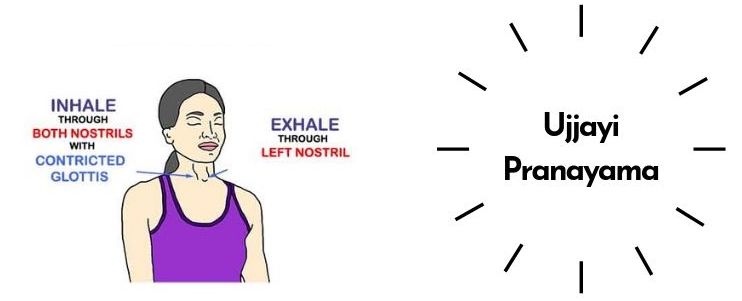 |
UJJAYI PRANAYAMA (Victorious Breath)
Ujjayi means "victorious" in Sanskrit. It involves constricting the glottis (vocal cords) at the back of the throat to create a sound like "sa" during inhalation and "ham" during exhalation. The air passing through the glottis creates a sound similar to ocean waves, known as Ajapa Mantra. It’s commonly used in Ashtanga and Vinyasa yoga.
Benefits of Ujjayi Pranayama:
- Calms the mind and body during practice.
- Generates heat in the body, promoting circulation.
- Regulates the nervous system and relieves stress.
- Can improve sleep when practiced before bed, especially combined with Shavasana.
- Helps lower heart rate and benefits those with high blood pressure.
Practice Method:
1. Sit, stand, or lie comfortably.
2. Gently close your lips and breathe through your nose, slightly constricting the back of your throat.
3. Guide your breath over your vocal cords, keeping it steady, deep, and long.
4. Listen for the ocean-like sound of your breath as it moves in and out. 5. Start by matching inhalation and exhalation lengths (1:1 ratio), and adjust according to comfort.
|
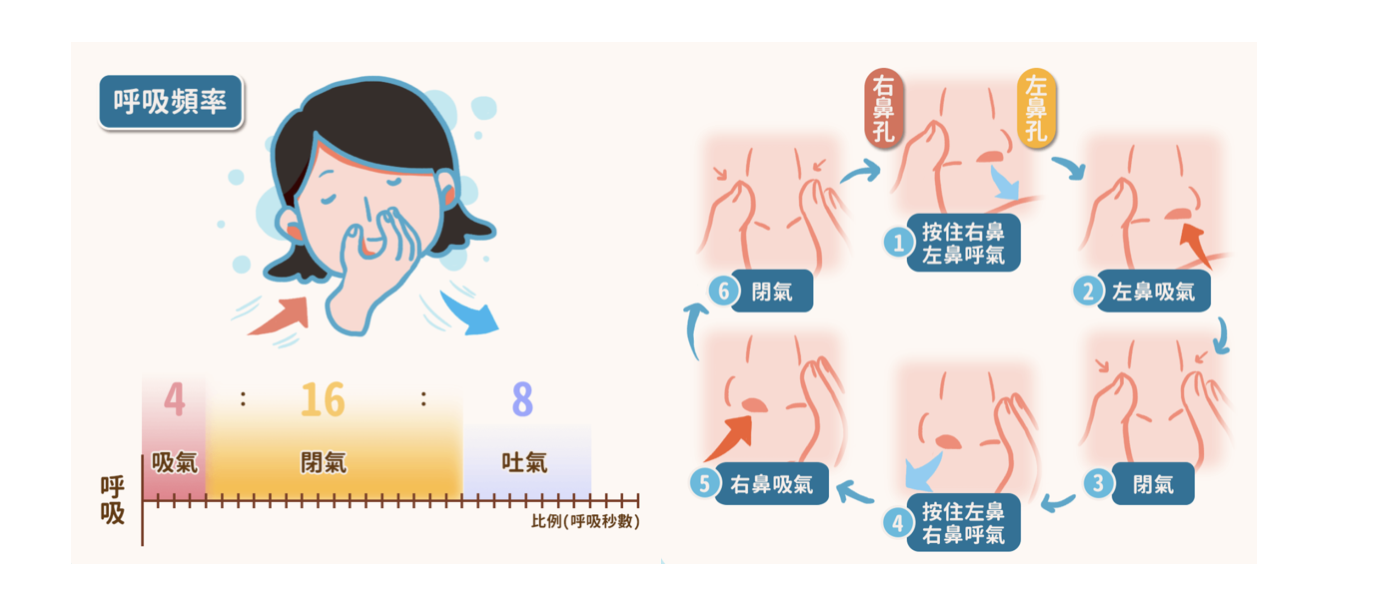 |
Nadi Shodhana Pranayama (Alternate Nostril Breathing)
Nadi Shodhana is a powerful breathing exercise with numerous benefits. "Nadi" means "channel" or "flow," and "shodhana" means "purification." This practice clears and balances the subtle energy channels of the body.
Benefits of Nadi Shodhana:
- Cleanses the Respiratory System**: Helps alleviate congestion and clear the airways.
- Improves Focus: Enhances mental clarity and concentration by stimulating brain circulation.
- Balances Energy: Ensures the body’s yin and yang energies are in harmony, essential for health.
- Strengthens Left and Right Brain Balance**: Helps balance the functions of both hemispheres of the brain.
- Soothes the Nervous System**: Reduces stress and helps prevent nervous system disorders.
Practice Method:
1. Use your right thumb to close your right nostril, exhale fully through the left nostril.
2. Inhale through the left nostril, then close it with your ring finger.
3. Release the thumb and exhale through the right nostril.
4. Inhale through the right nostril and close it again with the thumb.
5. Repeat the cycle, alternating nostrils.
Nadi Shodhana activates the entire brain, stimulating the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes calm. Practicing this breath technique for 10 minutes or more can have significant effects, making it an ideal tool for beginners in meditation and for overall health benefits.
|
|



